Business Integration: Connecting Systems for Seamless Operations

Introduction
In today's interconnected business world, organizations rely on multiple systems, applications, and platforms to manage their operations. Business integration is the process of connecting these disparate systems to enable seamless data flow and process automation. This blog explores the importance of business integration, key approaches, and best practices for successful implementation.
What is Business Integration?
Business integration refers to the linking of various business systems, applications, and data sources to function as a coordinated whole. It enables different parts of an organization to share data and communicate effectively, breaking down silos and improving operational efficiency.
The primary goal of business integration is to create a unified ecosystem where information flows freely between systems, enabling better decision-making, improved customer experiences, and streamlined business processes.
Types of Business Integration
1. Data Integration: Data integration involves combining data from different sources to provide a unified view. This enables organizations to access comprehensive information for analysis and reporting, breaking down data silos that often exist between departments.
2. Application Integration: Application integration connects different software applications to work together seamlessly. This allows data to flow between applications automatically, reducing manual data entry and minimizing errors.
3. Process Integration: Process integration focuses on automating and coordinating business processes across different systems and departments. This ensures that workflows are executed efficiently and consistently.
4. B2B Integration: Business-to-Business integration enables companies to exchange data and conduct transactions with partners, suppliers, and customers electronically, streamlining supply chain operations.
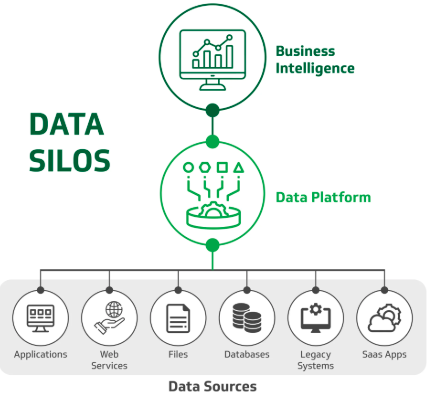
Benefits of Business Integration
Effective business integration transforms isolated systems into a cohesive digital ecosystem, driving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling organizations to respond quickly to market changes.
Improved Operational Efficiency: By automating data transfer and process workflows, business integration eliminates manual tasks, reduces errors, and speeds up operations. Employees can focus on value-added activities rather than repetitive data entry tasks.
Enhanced Decision Making: Integrated systems provide a comprehensive view of business data, enabling better-informed decisions. Real-time access to accurate information across the organization supports strategic planning and tactical execution.
Better Customer Experience: Integration enables a 360-degree view of customers by combining data from sales, marketing, support, and other touchpoints. This comprehensive understanding allows for personalized service and improved customer satisfaction.
Cost Reduction: Automated processes and reduced manual intervention lead to significant cost savings. Integration also helps avoid duplicate data entry and reduces the risk of costly errors.
Scalability and Flexibility: Integrated systems can easily accommodate new applications and technologies as business needs evolve. This flexibility ensures that the organization can adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Key Integration Approaches
API-Based Integration: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) provide a standardized way for applications to communicate. RESTful APIs have become the de facto standard for modern integration solutions, offering flexibility and ease of use.
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB): ESB is a middleware solution that facilitates communication between applications. It provides a central hub for message routing, transformation, and orchestration.
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service): Cloud-based integration platforms offer pre-built connectors and tools for integrating cloud and on-premises applications. These platforms simplify integration and reduce implementation time.
Event-Driven Architecture: This approach uses events to trigger and communicate between services. It's particularly effective for real-time integration scenarios and microservices architectures.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
1. Start with Clear Objectives: Define specific business goals and outcomes you want to achieve through integration. This helps prioritize integration projects and measure success.
2. Choose the Right Integration Pattern: Select integration approaches that align with your technical requirements, existing infrastructure, and future needs. Consider factors like real-time vs. batch processing, data volume, and system capabilities.
3. Implement Robust Security: Ensure that all integrations include proper authentication, authorization, and encryption. Protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
4. Plan for Monitoring and Maintenance: Implement comprehensive monitoring to track integration performance, identify issues quickly, and ensure reliability. Regular maintenance and updates are essential for long-term success.
5. Document Everything: Maintain detailed documentation of integration architectures, data flows, and dependencies. This knowledge is crucial for troubleshooting and future enhancements.
Conclusion
Business integration is no longer optional—it's a necessity for organizations looking to compete in today's digital economy. By connecting systems, automating processes, and enabling seamless data flow, business integration drives efficiency, improves decision-making, and enhances customer experiences. Success requires careful planning, the right technology choices, and a commitment to ongoing maintenance and optimization. With the proper approach, business integration can transform your organization's operations and unlock new opportunities for growth.






Leave A Comment